Heat changes often accompany chemical reactions. If heat is absorbed in a chemical reaction (endothermic
change), the products will have more energy than the reactants and 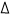 H will have a positive value. If heat is released in a chemical reaction (exothermic
change), the products will have less energy than the reactants and H will have a positive value. If heat is released in a chemical reaction (exothermic
change), the products will have less energy than the reactants and 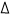 H will have a negative value. Regardless of whether a chemical reaction is endothermic or exothermic, all reactions require activation energy in order to begin. Activation
energy(Ea) is defined as the amount
of energy needed to start a chemical reaction. A catalyst is
sometimes used to reduce the amount of activation energy needed to start
a reaction. Catalysts are used to speed up reactions but are not used up
in the reaction. H will have a negative value. Regardless of whether a chemical reaction is endothermic or exothermic, all reactions require activation energy in order to begin. Activation
energy(Ea) is defined as the amount
of energy needed to start a chemical reaction. A catalyst is
sometimes used to reduce the amount of activation energy needed to start
a reaction. Catalysts are used to speed up reactions but are not used up
in the reaction.
To calculate the change in enthalpy (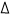 H)
for a reaction you must find the difference between the heats of formation
of the reactants and the products. H)
for a reaction you must find the difference between the heats of formation
of the reactants and the products.
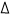 H
= Hf(products) – Hf(reactants) H
= Hf(products) – Hf(reactants)
|
For example:
Calculate the
change in enthalpy for the following reaction:
Ca + H2O  Ca(OH)2
+ H2 Ca(OH)2
+ H2
First balance the equation:
Ca + 2 H2O  Ca(OH)2
+ H2 Ca(OH)2
+ H2
Determine the enthalpy for the products and the reactants:
Ca + 2 H2O  Ca(OH)2
+ H2 Ca(OH)2
+ H2
0 + 2 (-286)  -986.6
+ 0 -986.6
+ 0
-572  -986.6 -986.6
|
Substance |
Hformation
(kJ/mol) |
Ca (s) |
0.0 |
H2O (l) |
-286 |
Ca(OH)2 (s) |
-986.6 |
H2 (g) |
0
|
|
| Note that only compounds have heat of formation values. All elements have heat of formation values of 0 kJ/mole. |
|
Calculate the 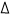 H
for the reaction using the formula from above: H
for the reaction using the formula from above:
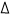 H = Hf(products) – Hf(reactants) H = Hf(products) – Hf(reactants)
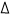 H = -986.6 – (-572) H = -986.6 – (-572)
 H = -414.6 kJ; this is
an exothermic reaction H = -414.6 kJ; this is
an exothermic reaction |

